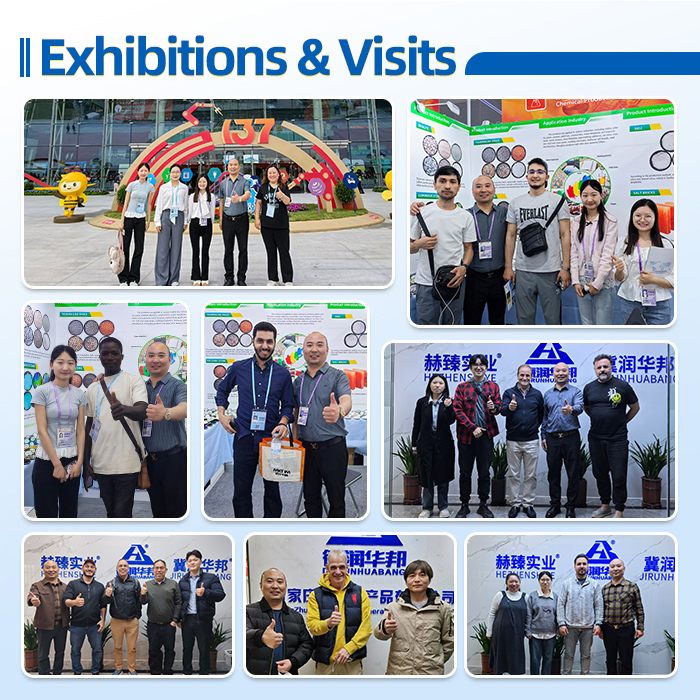
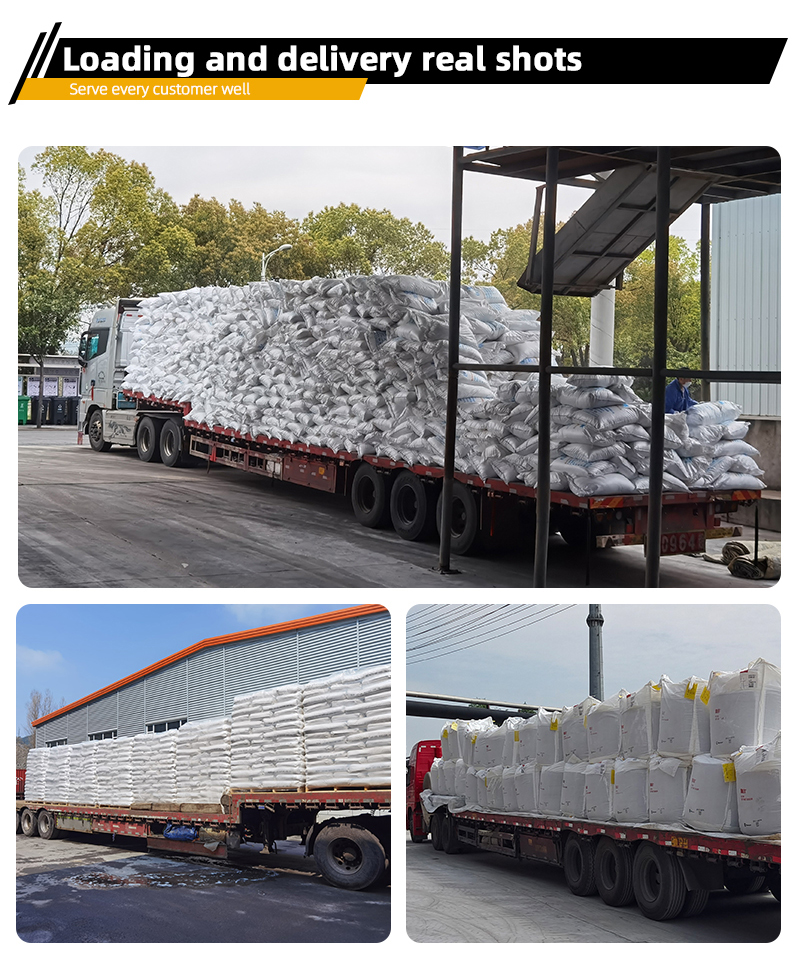
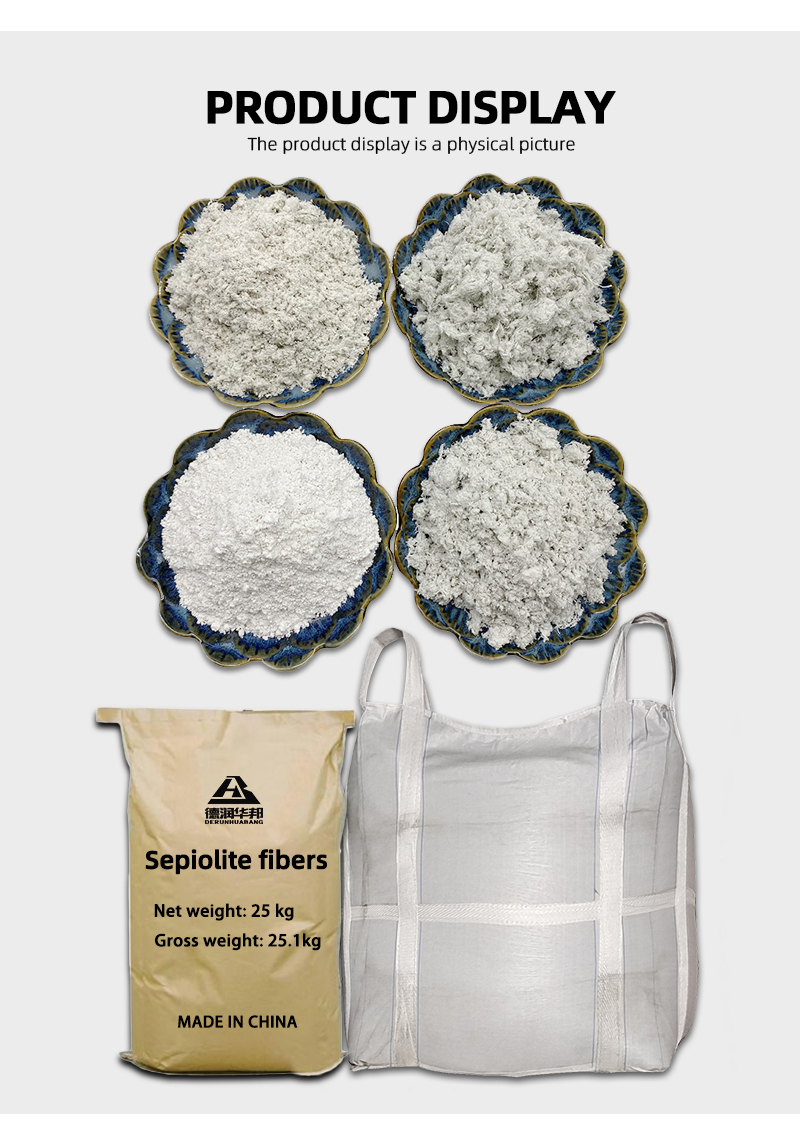
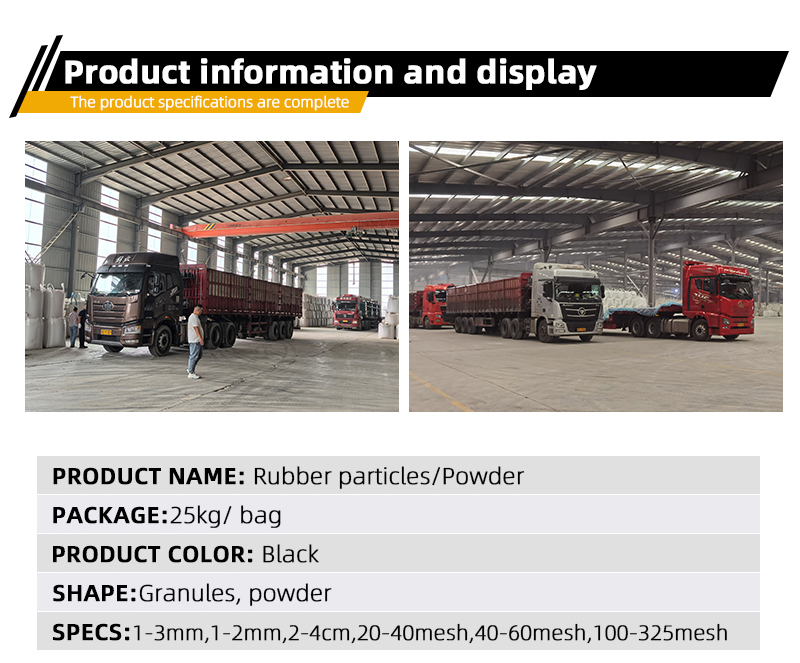
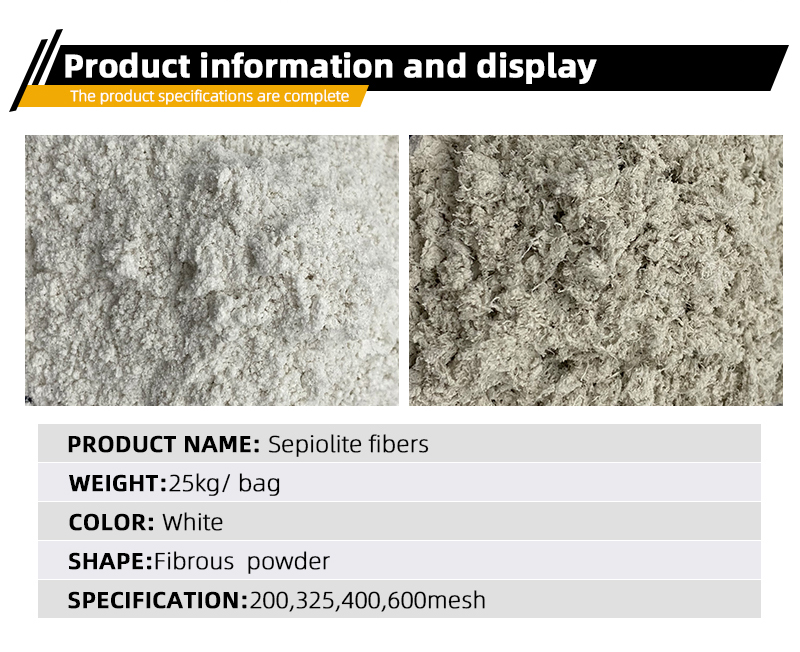
-

Tourmaline powder reinforces coating adhesion boosts coating wear resistance improves coating surface stability enhances coating weather tolerance optimizes coating application
Tourmaline powder serves as a premium functional additive that transforms the performance and longevity of industrial coating formulations, bringing targeted material advantages that address common pain points in coating production and application across diverse industrial settings. This finely processed mineral powder, crafted from natural tourmaline deposits through meticulous grinding and purification workflows, boasts consistent particle size, stable chemical properties, and strong compatibility with coating base materials, making it a pivotal ingredient for enhancing coating performance without venturing into restricted application fields. Every integration of tourmaline powder into coating mixtures centers on elevating core coating traits, from application workability to long-term durability, ensuring coated surfaces maintain reliable performance even under harsh industrial operating conditions and extending the service life of coated components and structures.One of the most impactful contributions of tourmaline powder to coating formulations is its ability to strengthen adhesion between the coating layer and substrate surfaces, a critical factor in preventing premature coating failure and ensuring long-lasting protection. When dispersed evenly within coating binders and resins, tourmaline powder creates microscale anchoring points that bond the coating firmly to metal, ceramic, polymer, and composite substrates, eliminating issues such as peeling, flaking, or blistering that plague standard coatings over time. This enhanced adhesion is especially valuable for industrial coatings applied to machinery, equipment casings, and structural surfaces that face frequent friction, vibration, and environmental exposure, as it keeps the coating intact and maintains continuous surface protection. Coating manufacturers rely on tourmaline powder to eliminate adhesion failures, reducing the need for frequent recoating and cutting down on maintenance costs for industrial end users.Tourmaline powder also significantly boosts the wear resistance of cured coating layers, making coated surfaces far more resilient to physical abrasion, scratching, and surface damage in heavy-use industrial environments. The rigid mineral structure of tourmaline powder reinforces the coating’s internal framework, increasing surface hardness and resistance to mechanical wear caused by daily handling, material contact, and industrial operations. Unlike softer coating additives that break down under friction, tourmaline powder retains its structural integrity within the coating matrix, preserving the smoothness and protective qualities of the coated surface even with prolonged use. This wear-resistant property makes coatings infused with tourmaline powder ideal for industrial surfaces that endure constant wear, such as production equipment exteriors, conveyor components, and workshop structural parts, ensuring the coating remains functional and visually intact for extended periods.In addition to mechanical durability, tourmaline powder enhances the weather tolerance of industrial coatings, shielding coated surfaces from damage caused by environmental stressors like temperature fluctuations, moisture exposure, and chemical contact. The inert chemical nature of tourmaline powder prevents reactive degradation within the coating, resisting breakdown from mild industrial chemicals, humidity, and extreme temperature shifts that commonly weaken standard coatings. This weather-resistant trait ensures the coating maintains its protective and aesthetic properties regardless of environmental conditions, whether applied to indoor industrial machinery or outdoor structural surfaces. Coatings enhanced with tourmaline powder do not fade, crack, or deteriorate due to environmental exposure, providing consistent, reliable protection for coated assets and reducing the risk of substrate corrosion or damage over time.Tourmaline powder optimizes the application flow and workability of liquid coating formulations, simplifying manufacturing and application processes for coating producers and applicators alike. The fine, uniform particles of tourmaline powder improve the rheological properties of coating mixtures, preventing pigment and filler settling during storage and transportation and ensuring a homogeneous, consistent texture throughout the formulation. This improved flow allows for smooth, even application via brushing, spraying, or rolling, eliminating streaks, uneven coverage, and patchy finishes that compromise coating quality. The enhanced workability also speeds up application workflows, reduces material waste from uneven coverage, and ensures that every coated surface receives a uniform layer of coating, maximizing both protective performance and visual appeal of the finished coating.Beyond application and durability, tourmaline powder refines the surface uniformity and finish quality of cured coatings, delivering a consistent, polished surface that meets strict industrial coating standards. The mineral particles fill microscale voids and imperfections within the coating layer, creating a smooth, flat surface that enhances the overall finish and eliminates uneven texture or blemishes. This uniform finish not only improves the visual appearance of coated industrial components but also reduces the accumulation of dust, debris, and contaminants on the surface, making coated equipment and structures easier to clean and maintain. For industrial coatings that require both functional protection and a professional aesthetic, tourmaline powder serves as a key additive that balances performance and visual quality, meeting the dual demands of industrial users.The compatibility of tourmaline powder with a wide range of coating base materials further solidifies its value in industrial coating production, as it blends seamlessly with water-based, solvent-based, and resin-based coating formulations without causing separation or chemical reactions. This universal compatibility allows coating manufacturers to incorporate tourmaline powder into existing production lines without overhauling formulas or processes, making it a cost-effective upgrade for enhancing coating performance. Whether used in protective industrial coatings, decorative machinery coatings, or specialized surface treatments, tourmaline powder integrates smoothly with all core coating components, preserving the base coating’s properties while amplifying its key performance traits to suit diverse industrial coating needs.Wastewater purification is an important and growing application of tourmaline powder, leveraging its adsorption capacity and polarization properties to treat industrial wastewater. Tourmaline powder effectively adsorbs heavy metal ions, organic pollutants, and suspended particles from wastewater, reducing contamination levels and improving water quality. Its polarization effect activates water molecules, enhancing the breakdown of organic contaminants and boosting adsorption efficiency. Tourmaline powder can be used as a filter medium in wastewater treatment systems or added directly to wastewater as a purification agent. It is particularly effective for treating industrial wastewater from manufacturing, mining, and chemical processing, helping industries meet environmental discharge standards. This application highlights tourmaline powder’s role in supporting industrial environmental compliance without involving restricted sectors.Tourmaline powder finds utility in the rubber industry as a reinforcing and functional additive, improving the performance of rubber products. When mixed into rubber compounds, it enhances tensile strength, tear resistance, and abrasion resistance, making rubber products more durable and resilient. It also improves rubber heat resistance and aging resistance, extending service life in high-temperature or harsh environments. Tourmaline powder’s polarization effect can reduce static buildup on rubber surfaces, making it suitable for rubber products used in electronic or explosive environments. Common applications include industrial rubber hoses, conveyor belts, and rubber gaskets, where strength and reliability are critical. This use of tourmaline powder helps rubber manufacturers produce high-performance products at a lower cost.Consistency in tourmaline powder quality also plays a vital role in reliable coating production, with standardized processing ensuring uniform particle size, purity, and performance across every batch. This batch-to-batch consistency eliminates variations in coating performance, allowing manufacturers to maintain strict quality control and produce coatings with predictable, repeatable results. For industrial coating applications that demand unwavering reliability, such as heavy machinery coatings and industrial facility surface treatments, this consistency is indispensable, ensuring that every batch of coating delivers the same enhanced adhesion, wear resistance, and weather tolerance. Coating producers can count on tourmaline powder to uphold product standards, streamline quality checks, and deliver high-performance coatings that meet the rigorous demands of industrial clients.The long-term structural stability of coatings containing tourmaline powder further adds to its industrial value, as the mineral additive does not break down, leach, or degrade within the coating matrix over time. Unlike organic additives that may deteriorate and reduce coating performance, tourmaline powder maintains its reinforcing properties throughout the coating’s service life, sustaining high levels of adhesion, wear resistance, and weather tolerance for years. This long-lasting stability means coated surfaces require less frequent maintenance, recoating, and repair, translating to significant cost savings for industrial operators and minimizing downtime associated with coating upkeep. For businesses seeking durable, low-maintenance coating solutions, tourmaline powder is an essential additive that delivers lasting value and reliable protection.The adaptability and multifunctionality of tourmaline powder drive sustained demand across industrial sectors. Its ability to enhance product performance, reduce costs, and add unique functional properties makes it an indispensable material in polymer composites, adhesives, coatings, wastewater treatment, and beyond. Unlike restricted materials, tourmaline powder offers a safe, cost-effective solution for improving industrial product quality and efficiency. With ongoing advancements in processing technology and product customization, tourmaline powder is poised to play an even greater role in industrial innovation, supporting the development of high-performance, durable, and environmentally compliant products for years to come.In summary, tourmaline powder stands as an indispensable functional additive for industrial coating formulations, offering a comprehensive suite of performance enhancements that elevate adhesion, wear resistance, weather tolerance, application flow, and finish quality. Its unique mineral properties and broad compatibility make it a versatile choice for coating manufacturers aiming to produce high-performance, durable coatings for industrial surfaces, addressing key challenges in coating performance and longevity. As industrial coating demands continue to rise for stronger, more resilient surface protection, tourmaline powder remains a top-tier additive that drives coating excellence, ensuring coated assets receive superior protection and maintaining operational efficiency across industrial sectors. The widespread integration of tourmaline powder into coating production underscores its role as a game-changing ingredient for modern industrial coating solutions, delivering consistent, impactful results for every coating application. -

Bentonite powder versatile binding agent enhancing mold strength surface finish collapsibility and production stability in ferrous
Bentonite powder is a naturally occurring clay mineral formed through the long-term geological alteration of volcanic ash and silicate rocks, boasting a unique layered crystalline structure that underpins its exceptional performance in industrial applications, most notably within the foundry sector. This fine, soft powder carries inherent properties such as strong water absorption, remarkable swelling capacity, superior binding ability, excellent thermal stability, and uniform dispersibility, all of which make it an irreplaceable raw material in modern foundry operations. Bentonite powder serves as the core binding component in foundry molding sand systems, acting as the backbone that holds sand particles together to form robust, dimensionally accurate molds and cores for metal casting processes. Its role in the foundry industry extends far beyond simple binding, influencing every stage of casting production, from sand mixing and mold shaping to molten metal pouring, solidification, and shakeout, directly impacting the quality of finished castings, production efficiency, and overall operational costs for foundries worldwide.In the foundry industry, bentonite powder is predominantly utilized in green sand molding, the most widely adopted casting method across global manufacturing, relied upon for producing a vast array of ferrous and non-ferrous metal castings. Green sand, composed primarily of silica sand, bentonite powder, water, and minor auxiliary additives, depends entirely on bentonite powder to create the cohesive bond between individual sand grains. When bentonite powder is mixed with water, its layered structure swells significantly, forming a thin, sticky film that coats each sand particle and fuses them into a cohesive mass. This bonding mechanism is reversible and flexible, allowing the green sand mixture to be easily molded into intricate shapes, compacted uniformly, and retain its form during handling, transportation, and the critical molten metal pouring phase. Without bentonite powder, green sand molding would be unfeasible, as loose sand lacks the structural integrity to withstand the extreme heat and pressure of molten metal, leading to mold collapse, casting defects, and failed production runs.The binding performance of bentonite powder directly dictates the green strength of foundry molds, a key parameter that defines the mold’s ability to maintain its shape and resist deformation during manual and mechanical handling. High-quality bentonite powder forms a strong yet pliable bond between sand particles, ensuring molds do not crack, chip, or lose dimensional accuracy when being moved from molding stations to pouring lines, or when positioned within casting flasks. This robust green strength is vital for both small-scale manual foundries and large-scale automated casting lines, where consistent mold integrity is essential to minimize production disruptions and reject rates. Bentonite powder with optimal swelling and binding properties ensures that even complex molds with thin sections, deep cavities, and delicate contours hold their shape perfectly, enabling the production of intricate castings used in automotive, machinery, construction, and industrial equipment sectors.Beyond green strength, bentonite powder contributes significantly to the hot strength of foundry molds, a critical characteristic that allows molds to withstand the searing temperatures of molten metal without breaking down or deforming. When molten iron, steel, or non-ferrous metals such as aluminum and copper are poured into molds, the intense heat rapidly evaporates residual moisture in the green sand and triggers thermal changes in the bentonite powder binder. High-grade bentonite powder maintains its structural stability under these extreme thermal conditions, preventing the mold wall from collapsing, eroding, or cracking as the molten metal fills the mold cavity and solidifies. This hot strength ensures that the casting retains the exact shape and dimensions of the mold, eliminating defects like metal penetration, sand inclusions, and dimensional distortion that would render castings unusable. Foundries rely on bentonite powder to deliver consistent hot strength across all casting runs, ensuring every piece meets strict dimensional and quality standards.Another indispensable property of bentonite powder in foundry applications is its excellent collapsibility, which simplifies the post-casting shakeout process and reduces labor and equipment wear. After the molten metal solidifies and cools to a manageable temperature, the bonded sand mold must be broken apart to extract the finished casting, and the sand recycled for reuse. Bentonite powder’s binding structure weakens predictably as the mold cools, allowing the sand to break down easily under mechanical vibration or impact during shakeout, without leaving stubborn, hardened sand residues stuck to the casting surface. This superior collapsibility not only speeds up production flow by reducing time spent on casting extraction but also minimizes damage to castings during demolding, such as scratches, dents, or broken edges. Additionally, bentonite powder facilitates efficient sand reclamation, as the broken-down sand can be easily screened, cleaned, and re-mixed with fresh bentonite powder and water, reducing raw material waste and lowering ongoing production costs for foundries of all sizes.Bentonite powder also plays a pivotal role in improving the surface finish of cast metal parts, a key quality metric that determines the suitability of castings for final use without extensive secondary machining. The fine particle size and uniform dispersibility of bentonite powder ensure that the green sand mixture forms a smooth, dense mold surface with minimal porosity and irregularities. When molten metal flows into this smooth mold cavity, it replicates the mold’s surface texture accurately, resulting in castings with clean, even surfaces free from sand pits, rough patches, and other surface flaws. This enhanced surface finish reduces the need for costly and time-consuming machining, grinding, and polishing operations, streamlining the production process and improving overall productivity. For precision castings used in automotive engines, hydraulic systems, and precision machinery, the smooth surface finish enabled by bentonite powder is critical to ensuring proper fit, function, and performance of the final component.In the production of foundry cores, which are used to create internal cavities, holes, and complex internal geometries in castings, bentonite powder serves as a reliable binding agent for core sand mixtures. Cores face even more demanding conditions than external molds, as they are fully surrounded by molten metal and exposed to prolonged high temperatures during casting. Bentonite powder provides the necessary strength and thermal stability for cores, preventing them from shifting, breaking, or disintegrating during metal pouring and solidification. This ensures that internal features of castings are accurately formed, with consistent dimensions and smooth internal surfaces. Bentonite powder-based core sand mixtures are easy to prepare, mold, and bake, offering a cost-effective alternative to resin-bonded cores for many standard casting applications, making it a staple in both small jobbing foundries and large-scale production foundries.The adaptability of bentonite powder makes it suitable for all types of metal casting processes within the foundry industry, covering ferrous metals like gray iron, ductile iron, and carbon steel, as well as non-ferrous metals including aluminum alloys, brass, and bronze. Each metal type requires specific mold properties, and bentonite powder can be tailored to meet these unique demands by adjusting the mixing ratio with sand and water, or by using specially processed bentonite powder grades. For iron casting, which involves extremely high molten metal temperatures, bentonite powder provides exceptional hot strength and thermal stability to prevent mold failure. For aluminum and other non-ferrous metal casting, bentonite powder delivers smooth mold surfaces and excellent collapsibility, ensuring high-quality, defect-free castings with fine surface details. This versatility eliminates the need for multiple specialized binding agents, simplifying foundry raw material management and reducing operational complexity.Different grades of bentonite powder are processed to meet the diverse needs of the global foundry industry, with each grade formulated to deliver specific performance attributes for different casting applications. Sodium bentonite powder, the most commonly used grade in foundries, offers superior swelling capacity, binding strength, and thermal stability, making it ideal for high-volume, high-temperature ferrous metal casting operations. Its strong water absorption and binding properties ensure consistent mold strength and performance, even in large-scale automated foundry lines. Calcium bentonite powder, while having slightly lower swelling capacity, provides good binding performance and cost efficiency, making it suitable for small-scale foundries, non-ferrous metal casting, and applications where extreme high-temperature resistance is not required. Activated bentonite powder, processed to enhance its binding and swelling properties, offers premium performance for precision casting, thin-walled castings, and complex component production, where mold quality and casting accuracy are paramount.The processing and quality control of bentonite powder for foundry use are rigorous, ensuring it meets the strict performance standards required for consistent casting results. Raw bentonite ore is extracted from carefully selected mineral deposits, then crushed, ground into a fine powder, and purified to remove impurities such as gravel, organic matter, and other minerals that could compromise its binding performance. The particle size of bentonite powder is tightly controlled, as finer particles ensure better dispersion in sand mixtures, more uniform coating of sand grains, and stronger mold strength. Purified bentonite powder is then tested for key properties including swelling index, binding capacity, moisture content, and thermal stability, with only batches meeting strict quality specifications approved for foundry use. This stringent quality control ensures that every batch of bentonite powder delivers consistent performance, allowing foundries to maintain stable production processes and minimize casting defects.Proper handling and storage of bentonite powder are essential to preserve its performance in foundry applications, as moisture contamination and physical degradation can impair its swelling and binding properties. Bentonite powder should be stored in dry, well-ventilated warehouse facilities, sealed in moisture-proof packaging to prevent exposure to humidity, rain, and water spillage. Excess moisture absorption causes bentonite powder to clump, reducing its dispersibility in sand mixtures and weakening mold strength. During transportation, bentonite powder must be protected from physical damage to packaging, ensuring the powder remains free-flowing and easy to mix. Foundries typically store bentonite powder in controlled conditions close to molding stations, ensuring quick access and maintaining its quality until use. Following proper storage protocols ensures that bentonite powder retains its full functional properties, delivering reliable binding performance every time it is mixed into molding sand.The mixing process of bentonite powder with silica sand, water, and other additives is a critical step in foundry operations, directly impacting the quality of the green sand mixture and subsequent casting results. Bentonite powder must be mixed uniformly with dry sand first to ensure even distribution, followed by the gradual addition of water to activate the powder’s swelling and binding properties. Over-mixing or under-mixing can lead to inconsistent mold strength, with under-mixed bentonite powder failing to bind sand particles effectively, and over-mixing causing excessive compaction and reduced mold permeability. Modern foundries use automated sand mixing systems to ensure precise control over mixing time, speed, and ingredient ratios, optimizing the performance of bentonite powder and producing consistent green sand batches.In summary, bentonite powder stands as an indispensable cornerstone of the global foundry industry, serving as the primary binding agent for green sand molding and enabling the efficient, cost-effective production of high-quality metal castings. Its unique combination of strong binding capacity, excellent swelling properties, thermal stability, balanced permeability, and superior collapsibility makes it uniquely suited to meet the rigorous demands of ferrous and non-ferrous metal casting. From small-scale artisanal foundries to large-scale automated manufacturing facilities, bentonite powder plays a vital role in shaping every stage of the casting process, directly influencing casting quality, production efficiency, and operational sustainability. -

Calcined kaolin clay for ceramics production paper coating plastic filler rubber enhancement and paint formulation supporting industrial manufacturing
Kaolin powder is a naturally occurring non-metallic mineral powder, primarily composed of kaolinite, formed through long-term weathering, hydrothermal alteration, and metamorphism of aluminosilicate rocks. This mineral powder is widely used across multiple industrial sectors due to its unique combination of physical and chemical properties, making it an indispensable material in modern manufacturing. Processing of kaolin powder involves a series of systematic steps: crushing raw kaolin ore into coarse particles, removing impurities through physical separation methods, grinding to achieve desired fineness, and optional calcination or surface modification to enhance its functional properties.The industrial value of kaolin powder is rooted in its core properties, including high whiteness, excellent plasticity, chemical inertness, thermal stability, and low oil absorption. Whiteness is one of the most distinctive traits of kaolin powder, making it highly desirable in industries that require bright, uniform, and consistent finishes. Natural kaolin powder possesses inherent whiteness, which can be further enhanced through purification and bleaching processes to meet the strict requirements of high-end applications. Plasticity allows kaolin powder to be easily shaped and molded when mixed with water, maintaining its form during drying and firing, which is critical for processes like ceramics production. Chemical inertness ensures that kaolin powder does not easily react with other substances, making it a safe and reliable additive in various manufacturing processes, even in harsh industrial environments.Ceramics production is one of the oldest and most important applications of kaolin powder, serving as a key raw material in both traditional and advanced ceramic manufacturing. Kaolin powder’s plasticity enables ceramic manufacturers to create intricate shapes and designs, from everyday pottery and tableware to high-performance industrial ceramics. When mixed with water, kaolin powder forms a smooth, malleable paste that can be shaped into any form, and during firing, it undergoes chemical changes that enhance the strength, durability, and heat resistance of the final ceramic product. Calcined kaolin powder, which is heated at high temperatures to remove moisture and impurities, further improves the density and strength of ceramics, making it suitable for advanced ceramic components used in industrial equipment and electronic devices. Additionally, kaolin powder helps reduce firing temperature and shorten firing cycles, lowering energy consumption for ceramic manufacturers.The paper industry is another major consumer of kaolin powder, where it is used both as a filler and a coating material to improve paper quality and performance. As a filler, kaolin powder fills the gaps between paper fibers, enhancing paper opacity, smoothness, and printability. It also improves the tensile strength and stiffness of paper, reducing breakage during printing and handling. As a coating material, kaolin powder creates a smooth, uniform surface on paper, which enhances ink absorption and print clarity, making it ideal for high-quality printing papers, such as magazines, brochures, and packaging materials. Ultrafine kaolin powder is particularly suitable for paper coating due to its fine particle size, which ensures a smooth finish and excellent ink adhesion. Surface-modified kaolin powder further improves compatibility with paper fibers and coating binders, enhancing overall paper quality.Kaolin powder serves as an effective industrial filler in plastics and rubber manufacturing, where it enhances material performance while reducing production costs. In plastic production, kaolin powder is added to polymer matrices to improve tensile strength, flexural strength, and impact resistance, while also reducing shrinkage and warping during molding. Its chemical inertness ensures compatibility with various plastic resins, preventing unwanted reactions and maintaining material stability. In rubber manufacturing, kaolin powder acts as a reinforcing filler, improving the tensile strength, tear resistance, and abrasion resistance of rubber compounds. It also enhances the heat resistance and aging resistance of rubber products, extending their service life in harsh environments. Common applications include plastic packaging, automotive plastic parts, rubber seals, and industrial hoses, where durability and performance are critical.In the paint and coating industry, kaolin powder functions as a functional additive and extender, improving coating performance and reducing production costs. It enhances the opacity, viscosity, and leveling properties of paints, ensuring even application and a smooth, uniform finish. Kaolin powder also boosts the scratch resistance and wear resistance of coatings, extending the service life of painted surfaces. Its high whiteness contributes to bright, long-lasting paint colors, reducing the need for excessive amounts of expensive pigments. Calcined kaolin powder, with its improved hardness and chemical stability, is particularly suitable for high-performance coatings used in industrial equipment, architectural surfaces, and automotive applications. Additionally, kaolin powder’s chemical inertness ensures compatibility with other paint ingredients, preventing coating degradation and maintaining quality over time.Plastic industry widely uses kaolin powder as cost-effective reinforcement to upgrade comprehensive performance of basic plastics. When added to polypropylene and polyethylene (the most commonly used general-purpose plastics), it significantly enhances rigidity of plastic products—making them suitable for manufacturing household appliance casings (refrigerators, washing machines) and construction plastic profiles (door and window frames). It also improves heat resistance of plastics, enabling them to be used in manufacturing electrical component housings (which generate heat during operation) without deformation. Additionally, kaolin powder boosts dimensional stability of plastics, preventing warping or shrinking after molding—critical for precision plastic parts. Surface-modified kaolin powder can disperse evenly in polymer matrices, forming strong interfacial bonds that increase impact resistance while maintaining surface smoothness—essential for appearance-sensitive products (such as plastic decorative parts). Importantly, it is fully compatible with existing extrusion and injection molding processes, allowing manufacturers to use existing equipment without additional modifications or production costs.Other industrial applications of kaolin powder include its use in adhesives, sealants, and composite materials. In adhesives and sealants, kaolin powder improves bonding strength, viscosity, and thixotropy, ensuring better application properties and long-term stability. It also enhances the heat resistance and chemical resistance of adhesives, making them suitable for harsh industrial environments. In composite materials, kaolin powder is added to enhance thermal stability, mechanical strength, and dimensional stability, making composites suitable for a wide range of applications, from construction materials to electronic components. Surface-modified kaolin powder, treated with coupling agents, further improves compatibility with composite matrices, optimizing overall performance.The versatility and cost-effectiveness of kaolin powder drive sustained demand across industrial sectors. Its ability to enhance product performance, reduce production costs, and adapt to diverse applications makes it an indispensable material in ceramics, paper, plastics, rubber, paints, and composites. Unlike restricted sectors, kaolin powder’s industrial applications focus on improving manufacturing efficiency and product quality, aligning with modern industrial development trends. With ongoing advancements in processing technology and product customization, kaolin powder is poised to play an even more important role in industrial innovation, supporting the development of high-performance, durable products for years to come. -

Tourmaline powder with polarization mechanical strength heat resistance for polymer composite reinforcement adhesive additive coating modifier and wastewater purification aiding industrial production
Tourmaline powder is a mineral-based powder processed from natural tourmaline, a crystalline boron silicate mineral formed through geological activities involving magma crystallization, hydrothermal alteration, and metamorphic processes of aluminosilicate formations. This mineral powder is celebrated for its unique set of physical and chemical traits that make it a versatile additive and functional material across numerous industrial fields. Production of tourmaline powder involves systematic processing steps: crushing raw tourmaline ore into coarse particles, purifying to remove non-tourmaline impurities via physical separation methods, grinding to achieve targeted particle sizes, and surface treatment to enhance compatibility with various matrices. These processes yield distinct tourmaline powder types, such as ultrafine tourmaline powder, nano-tourmaline powder, surface-treated tourmaline powder, and natural tourmaline powder, each designed to fulfill specific functional needs in different industrial applications.Core properties of tourmaline powder underpin its widespread industrial adoption, with electrical polarization, mechanical strength, heat resistance, and adsorption capacity being key attributes. Electrical polarization of tourmaline powder arises from its piezoelectric and thermoelectric effects, enabling it to generate microelectrical fields when exposed to pressure or temperature fluctuations. This trait is valuable for applications requiring static dissipation or microelectric stimulation. Tourmaline powder also exhibits impressive mechanical strength, allowing it to act as a reinforcing agent that boosts the structural integrity of composite materials. Its heat resistance ensures stability even in high-temperature manufacturing processes, while strong adsorption capacity makes it effective for capturing contaminants and impurities. Together, these properties make tourmaline powder a multifunctional material that adds value to a wide range of industrial products.Polymer composite reinforcement is a primary application of tourmaline powder, where it enhances the performance of plastic, resin, and fiber composites. When integrated into polymer matrices, tourmaline powder improves tensile strength, flexural strength, and impact resistance, while minimizing shrinkage and improving dimensional stability. Ultrafine and nano-tourmaline powder variants offer superior dispersion capabilities, preventing particle agglomeration and ensuring uniform distribution throughout the composite. Surface-treated tourmaline powder, modified with coupling agents, forms stronger bonds with polymer molecules, further elevating composite durability and resistance to environmental degradation. This makes tourmaline powder a cost-effective alternative to high-priced reinforcing fibers, helping manufacturers improve product quality while reducing production expenses.Tourmaline powder serves as a reliable additive in adhesives and sealants, enhancing bonding performance and long-term stability. When added to adhesive formulations, it improves bonding strength to various substrates, including metals, plastics, and ceramics, while boosting heat resistance and chemical resistance. Tourmaline powder also enhances the viscosity and thixotropy of adhesives, ensuring better application properties and reducing sagging during curing. In sealants, it improves flexibility and wear resistance, extending service life in harsh industrial environments. Common uses include industrial adhesives for construction, automotive sealants, and high-temperature adhesive tapes, where reliable performance is essential. By incorporating tourmaline powder, manufacturers can produce adhesives and sealants that meet rigorous industrial standards.In coating formulations, tourmaline powder acts as a functional modifier that enhances coating performance and adds unique properties. It improves coating opacity, leveling, and adhesion, ensuring a smooth, uniform finish that resists peeling and cracking. Tourmaline powder also boosts scratch resistance and wear resistance of coatings, extending the service life of painted or coated surfaces. Its heat resistance makes it suitable for high-temperature coatings used in industrial equipment, while its adsorption capacity helps capture volatile organic compounds, improving coating environmental performance. Additionally, tourmaline powder’s polarization effect can reduce static buildup on coated surfaces, making it useful for electronic device coatings. These benefits make tourmaline powder a valuable additive in industrial coatings, architectural paints, and specialty coatings.Wastewater purification is an important and growing application of tourmaline powder, leveraging its adsorption capacity and polarization properties to treat industrial wastewater. Tourmaline powder effectively adsorbs heavy metal ions, organic pollutants, and suspended particles from wastewater, reducing contamination levels and improving water quality. Its polarization effect activates water molecules, enhancing the breakdown of organic contaminants and boosting adsorption efficiency. Tourmaline powder can be used as a filter medium in wastewater treatment systems or added directly to wastewater as a purification agent. It is particularly effective for treating industrial wastewater from manufacturing, mining, and chemical processing, helping industries meet environmental discharge standards. This application highlights tourmaline powder’s role in supporting industrial environmental compliance without involving restricted sectors.Tourmaline powder finds utility in the rubber industry as a reinforcing and functional additive, improving the performance of rubber products. When mixed into rubber compounds, it enhances tensile strength, tear resistance, and abrasion resistance, making rubber products more durable and resilient. It also improves rubber heat resistance and aging resistance, extending service life in high-temperature or harsh environments. Tourmaline powder’s polarization effect can reduce static buildup on rubber surfaces, making it suitable for rubber products used in electronic or explosive environments. Common applications include industrial rubber hoses, conveyor belts, and rubber gaskets, where strength and reliability are critical. This use of tourmaline powder helps rubber manufacturers produce high-performance products at a lower cost.Other industrial applications of tourmaline powder include its use in refractory materials and electronic components. In refractories, its heat resistance and chemical stability make it suitable for high-temperature furnaces, kilns, and industrial heaters, where it enhances refractory material durability and thermal insulation. In electronic components, nano-tourmaline powder is used to improve the performance of dielectric materials, capacitors, and static control devices, thanks to its polarization properties. Tourmaline powder also finds use in friction materials, where it improves wear resistance and reduces noise, making it suitable for brake pads and clutch plates. These diverse applications demonstrate the versatility of tourmaline powder and its importance in modern industrial manufacturing.Global tourmaline ore reserves ensure a stable supply of tourmaline powder for industrial needs, with major production regions focusing on advancing processing technologies. Innovations in ultra-fine grinding and surface modification have expanded the range of tourmaline powder products, enabling customization for specific industrial applications. Manufacturers prioritize quality control to ensure consistent particle size, purity, and performance across batches, making tourmaline powder a reliable material for industrial use. As industrial technologies evolve, new processing methods continue to unlock additional potential for tourmaline powder, expanding its application scope.The adaptability and multifunctionality of tourmaline powder drive sustained demand across industrial sectors. Its ability to enhance product performance, reduce costs, and add unique functional properties makes it an indispensable material in polymer composites, adhesives, coatings, wastewater treatment, and beyond. Unlike restricted materials, tourmaline powder offers a safe, cost-effective solution for improving industrial product quality and efficiency. With ongoing advancements in processing technology and product customization, tourmaline powder is poised to play an even greater role in industrial innovation, supporting the development of high-performance, durable, and environmentally compliant products for years to come.Electrical polarization, derived from piezoelectric and thermoelectric effects, is a defining trait of tourmaline powder, enabling microelectric field generation and static dissipation. Mechanical strength makes it an effective reinforcing agent, while heat resistance ensures stability in high-temperature processes. Adsorption capacity allows it to capture contaminants, making it suitable for purification applications. These properties work together to make tourmaline powder a multifunctional material that enhances product performance across diverse industrial sectors.Polymer composite reinforcement is a key application, with tourmaline powder boosting tensile, flexural, and impact strength of plastic and resin composites. Ultrafine and nano variants ensure uniform dispersion, while surface-treated tourmaline powder forms stronger bonds with polymers. This reduces production costs and improves composite durability, making it a viable alternative to expensive reinforcing materials. Tourmaline powder’s role in polymer composites helps manufacturers optimize product quality and competitiveness.As an adhesive and sealant additive, tourmaline powder improves bonding strength, heat resistance, and chemical resistance. It enhances adhesive viscosity and thixotropy, ensuring better application and curing properties, while boosting sealant flexibility and wear resistance. This makes it suitable for industrial adhesives and sealants used in construction, automotive, and high-temperature applications, where reliability is critical.In coatings, tourmaline powder acts as a modifier that improves opacity, adhesion, and scratch resistance. It enhances coating durability, heat resistance, and static control, making it useful for industrial, architectural, and electronic coatings. Its adsorption capacity also helps reduce volatile organic compounds, improving coating environmental performance without involving restricted sectors.Wastewater purification leverages tourmaline powder’s adsorption capacity and polarization effect to remove heavy metals, organic pollutants, and suspended particles. It activates water molecules to boost purification efficiency, making it effective for industrial wastewater treatment. This application helps industries meet environmental standards, supporting responsible industrial production.In the rubber industry, tourmaline powder reinforces rubber compounds, improving tensile strength, tear resistance, and heat resistance. It reduces static buildup and extends product service life, making it suitable for industrial rubber products like hoses, conveyor belts, and gaskets. This use helps rubber manufacturers produce durable products at lower costs.Additional applications include refractory materials, where tourmaline powder enhances heat resistance and durability, and electronic components, where nano-tourmaline powder improves dielectric performance and static control. Global tourmaline reserves ensure stable supply, with processing technologies advancing to produce customized tourmaline powder products for diverse industrial needs. -

Himalayan salt bricks charming natural pieces elevating warm modernism interior design boasting soft glow and textured charm for homes spas and commercial spaces
Himalayan Salt Bricks emerge as iconic decorative elements in contemporary spaces, blending natural charm with design versatility that suits both residential and commercial settings. Their delicate pink and amber hues, derived from ancient mineral deposits deep within mountain regions, bring unique character to any environment—shifting from soft pastels in natural light to warm golds under artificial illumination. Shades range from soft blush to rich terracotta, with subtle gradients that add dynamic layers to interiors without overwhelming existing decor. Crafted from raw salt blocks, these bricks retain organic textures—with faint crystalline patterns and uneven edges—that set them apart from synthetic decor materials, aligning perfectly with shifting preferences for authentic, nature-driven elements in modern interiors. Unlike mass-produced decor pieces, each Himalayan Salt Brick carries subtle variations in color and texture, ensuring every installation feels one-of-a-kind and deeply rooted in natural origins.Salt Walls built with Himalayan Salt Bricks have become standout focal points in warm modernism designs, offering a balance of coziness and sophistication. These structures transform ordinary rooms into inviting retreats, whether in private residences, boutique spas, cozy cafes or intimate hotel suites. Backlighting—installed behind thin layers of Himalayan Salt Bricks or integrated into wall cavities with dimmable fixtures—enhances the inherent beauty of these bricks, casting a soft, diffused ambient glow that creates a calm and cozy atmosphere. Light filters through mineral-rich surfaces, emitting warm tones that soften the sharp lines of modern furniture and neutral color palettes. Designers often pair such walls with wooden beams, woven textiles or linen fabrics to amplify a rustic yet refined vibe, making spaces feel grounded and serene. In living rooms, Salt Walls serve as striking backdrops for sofas or fireplaces, while in spa lobbies, they set a tranquil tone for relaxation-focused experiences, guiding guests into a state of calm from the moment they enter.Versatility of Himalayan Salt Bricks extends far beyond full-wall installations, with Salt Tiles cut from the same material offering endless decorative possibilities. These tiles serve as backsplashes, accent panels or floor inlays, adding subtle texture without disrupting the overall design harmony. Salt Tiles for kitchen backsplashes bring warm contrast to bright, functional spaces, pairing beautifully with light cabinetry, natural stone countertops and wooden kitchen islands. As accent panels, they can line niches, stairwells, headboards or even ceiling coves, infusing small, often-overlooked areas with natural charm. In spas and wellness centers, these tiles integrate seamlessly into holistic aesthetics, complementing natural elements like potted plants, river rocks, bamboo fixtures and soft linen drapes. Their ability to diffuse light gently makes them ideal for areas meant for relaxation and unwinding—such as massage rooms, meditation corners or yoga studios—where harsh lighting would disrupt the peaceful ambiance essential to wellness practices.Himalayan Salt Bricks also shine as versatile standalone decor pieces, crafted into functional and decorative items by skilled artisans. Artisans carve them into candle holders, small sculptures, display accents and even wall sconces, each piece boasting unique patterns and color variations that highlight the material’s natural beauty. Candle holders made from Himalayan Salt Bricks soften flame light, casting a warm pinkish glow that elevates evening ambiance—perfect for dinner parties, quiet reading nooks or bedside lighting. Small sculpted pieces—shaped into geometric forms, organic curves or abstract motifs—add visual interest to coffee tables, mantels, shelving units and entryway consoles, tying together design themes in living rooms, bedrooms, offices and hallways. These decor items adapt seamlessly to both casual and refined spaces: in bohemian-style bedrooms, they complement macramé wall hangings, layered rugs and potted succulents; in minimalist offices, they add subtle texture without cluttering clean surfaces or disrupting focus. The soft glow from candlelit salt holders creates an intimate ambiance for family gatherings, friend get-togethers or quiet evenings spent at home.Design flexibility of Himalayan Salt Bricks allows seamless adaptation to diverse styles beyond warm modernism, making them a versatile choice for any interior vision. For modern minimalist spaces, smooth-finish Salt Bricks offer a streamlined look that complements clean lines, simple furnishings and monochromatic color schemes, adding warmth without sacrificing minimalism’s core ethos of simplicity. Rustic interiors benefit from rough-hewn versions, which emphasize natural, unrefined beauty and pair effortlessly with reclaimed wood, wrought iron fixtures, vintage rugs and handcrafted decor. Industrial-style spaces integrate Himalayan Salt Bricks with exposed brick walls, metal fixtures and concrete surfaces, balancing edgy, urban aesthetics with soft, natural elements. Even commercial spaces like boutiques, bookstores and hotel lobbies use these bricks to craft memorable environments that resonate with customers seeking authentic, sensory experiences. Cafes often install Salt Brick accent walls behind counter areas or seating nooks, creating an inviting backdrop that encourages patrons to capture photos and share their visits online, boosting brand appeal through organic social media presence.Preserving the beauty of Himalayan Salt Bricks requires simple, low-effort care practices that fit busy lifestyles and high-traffic spaces. Keeping them away from excessive moisture prevents degradation, so they are best avoided in areas prone to water splashes—such as shower surrounds, kitchen sink edges or outdoor patios exposed to rain. In humid climates, occasional wiping with a dry, lint-free cloth helps maintain their texture and prevent moisture buildup, while in dry environments, a light dusting is all that’s needed to keep them looking fresh. Regular dusting with a soft brush or microfiber cloth preserves their natural luster, allowing mineral-rich colors to remain vibrant over time. Unlike high-maintenance decor materials that require frequent polishing, sealing or treatments, Himalayan Salt Bricks retain their beauty with minimal effort. Such low-maintenance quality makes them a practical choice for busy homes, rental properties, coworking spaces and high-traffic commercial areas alike, where durability and ease of care are essential considerations.Global interest in warm modernism and natural design elements has elevated Himalayan Salt Bricks to must-have decor items in recent years, with their popularity spanning across design trends and geographic regions. Their ability to infuse spaces with warmth, texture and unique visual appeal transcends fleeting trends, making them an enduring addition to any interior. Whether used to build striking Salt Walls, craft delicate accents or line serene spa interiors, these bricks bring a touch of mountain-inspired tranquility to any environment. Interior designers increasingly recommend Himalayan Salt Bricks to clients seeking to balance modern functionality with natural charm, as they bridge the gap between style and comfort seamlessly. As design preferences continue to prioritize comfort, authenticity and sensory experiences over overly polished aesthetics, Himalayan Salt Bricks remain a top choice for those seeking to transform spaces into havens of style and calm.Salt Tiles and bricks also offer extensive customization possibilities that cater to unique design visions, from subtle accents to bold statement pieces. Artisans can shape them into various sizes and configurations—from thin, lightweight panels for accent walls to thick, substantial blocks for floor installations or freestanding features—adapting to specific space requirements and design goals. Some artisans add subtle engravings, cutouts or geometric patterns to Himalayan Salt Bricks, creating designs that interact beautifully with light, casting intricate shadows and enhancing the material’s natural glow. From small, delicate accent pieces to large-scale full-wall installations, each application highlights the distinct qualities of Himalayan Salt Bricks. Their natural color variations—rooted in the mineral composition of the original salt deposits—ensure no two installations are identical, adding exclusivity and uniqueness to every project. This one-of-a-kind quality makes them beloved by designers and homeowners aiming to create personalized spaces that reflect individual taste, rather than cookie-cutter interiors. Custom Salt Brick installations often become conversation starters, adding a personal, memorable touch to homes, spas, boutiques and commercial venues alike.Beyond decorative use, Himalayan Salt Bricks also contribute to creating cohesive design narratives that tie spaces together. For open-concept homes, Salt Brick accent walls can define separate zones—such as dining areas or reading corners—without the need for physical dividers, maintaining an open feel while adding visual structure. In commercial spaces, they can reinforce brand aesthetics: boutique hotels use them to evoke a sense of calm and luxury, while cafes leverage their warm glow to create a welcoming, home-like atmosphere. Even in small apartments, compact Salt Brick installations—like niche liners or small wall panels—can add depth and character, proving that these versatile elements work in spaces of all sizes. Their ability to blend with diverse materials and styles ensures they remain relevant as design preferences evolve, solidifying their place as a timeless decor staple.Artisans who craft Himalayan Salt Bricks and tiles prioritize honoring the material’s natural properties, avoiding harsh treatments that alter its organic texture or color. The process of creating these bricks involves carefully cutting and shaping raw salt blocks, often by hand, to preserve their crystalline structure and unique variations. This artisanal approach not only maintains the material’s authenticity but also supports traditional craftsmanship, adding another layer of value to Himalayan Salt Brick installations. Homeowners and designers alike appreciate this connection to handcrafted quality, as it adds meaning to decor choices beyond mere aesthetics. Whether used in a minimalist apartment, a rustic cottage or a high-end spa, Himalayan Salt Bricks carry a sense of natural heritage and artisanal care that resonates with those seeking purposeful, intentional design.Salt Walls built with Himalayan Salt Bricks have become focal points in warm modernism designs. These structures transform ordinary rooms into inviting retreats, whether in private residences, boutique spas or cozy commercial venues. Backlighting—installed behind thin layers of Himalayan Salt Bricks or integrated into wall cavities—enhances inherent beauty of these bricks, casting soft ambient glow that creates calm and cozy atmosphere. Light filters through mineral-rich surfaces, emitting warm tones that soften sharp lines of modern furniture. Designers often pair such walls with wooden beams, woven textiles or neutral fabrics to amplify rustic yet sophisticated vibe, making spaces feel grounded and serene. In living rooms, Salt Walls serve as striking backdrops for sofas or fireplaces; in spa lobbies, they set tranquil tone for relaxation-focused experiences.Versatility of Himalayan Salt Bricks extends beyond full walls. Salt Tiles cut from same material serve as backsplashes, accent panels or floor inlays, adding subtle texture without overwhelming overall design. Salt Tiles for backsplashes bring warm contrast to kitchen spaces, pairing beautifully with light cabinetry and natural stone countertops. As accent panels, they can line niches, stairwells or headboards, infusing small areas with natural charm. In spas and wellness centers, these tiles integrate seamlessly into holistic aesthetics, complementing natural elements like potted plants, river rocks and bamboo fixtures. Their ability to diffuse light gently makes them ideal for areas meant for relaxation and unwinding, such as massage rooms or meditation corners, where harsh lighting would disrupt calm.Himalayan Salt Bricks also shine as standalone decor pieces. Artisans carve them into candle holders, small sculptures and display accents, each piece boasting unique patterns and color variations. Candle holders made from Himalayan Salt Bricks soften flame light, casting warm pinkish glow that elevates evening ambiance. Small sculpted pieces—shaped into geometric forms or organic curves—add visual interest to coffee tables, mantels and shelving units, tying together design themes in living rooms, bedrooms and offices. These decor items work well in both casual and refined spaces: in bohemian-style bedrooms, they complement macramé wall hangings and layered rugs; in minimalist offices, they add subtle texture without cluttering clean surfaces. Soft glow from candlelit salt holders creates intimate ambiance for family gatherings, friend get-togethers or quiet evenings at home.Design flexibility of Himalayan Salt Bricks allows adaptation to diverse styles beyond warm modernism. For modern minimalist spaces, smooth-finish Salt Bricks offer streamlined look that complements clean lines and simple furnishings, adding warmth without sacrificing minimalism’s core ethos. Rustic interiors benefit from rough-hewn versions, which emphasize natural, unrefined beauty and pair well with reclaimed wood, wrought iron and vintage decor. Industrial-style spaces integrate Himalayan Salt Bricks with exposed brick walls and metal fixtures, balancing edgy aesthetics with soft natural elements. Even commercial spaces like boutiques, cafes and hotel lobbies use these bricks to craft memorable environments that resonate with customers seeking authentic experiences. Cafes often install Salt Brick accent walls behind counter areas, creating inviting backdrop for patrons to capture photos and share online.Preserving beauty of Himalayan Salt Bricks requires simple care practices that fit busy lifestyles. Keeping them away from excessive moisture prevents degradation—so they are best avoided in areas prone to water splashes, like shower surrounds or kitchen sink edges. In humid climates, occasional wiping with dry cloth helps maintain their texture and prevent moisture buildup. Regular dusting with soft brush or microfiber cloth maintains their natural luster, allowing mineral-rich colors to remain vibrant over time. Unlike high-maintenance decor materials that require frequent polishing or treatments, Himalayan Salt Bricks retain their beauty with minimal effort. Such low-maintenance quality makes them practical choice for busy homes, rental properties and high-traffic commercial areas alike, where durability and ease of care are essential. Global interest in warm modernism and natural design elements has elevated Himalayan Salt Bricks to must-have decor items in recent years. Their ability to infuse spaces with warmth, texture and unique visual appeal transcends fleeting trends, making them enduring addition to any interior. Whether used to build striking Salt Walls, craft delicate accents or line serene spa interiors, these bricks bring touch of mountain-inspired tranquility to any environment. Interior designers increasingly recommend Himalayan Salt Bricks to clients seeking to balance modern functionality with natural charm, as they bridge gap between style and comfort. As design preferences continue to prioritize comfort and authenticity over overly polished aesthetics, Himalayan Salt Bricks remain enduring choice for those seeking to transform spaces into havens of style and calm.Salt Tiles and bricks also offer customization possibilities that cater to unique design visions. Artisans can shape them into various sizes and configurations—from thin panels for accent walls to thick blocks for statement pieces—adapting to specific space requirements. Some artisans add subtle engravings or cutouts to Himalayan Salt Bricks, creating patterns that interact beautifully with light. From small accent pieces to full-wall installations, each application highlights distinct qualities of Himalayan Salt Bricks. Their natural color variations ensure no two installations are identical, adding exclusivity to every project. This uniqueness makes them beloved by designers and homeowners aiming to create personalized spaces that reflect individual taste, rather than cookie-cutter interiors. Custom Salt Brick installations often become conversation starters, adding personal touch to homes and commercial venues alike.Salt Walls built with Himalayan Salt Bricks have become focal points in warm modernism designs. These structures transform ordinary rooms into inviting retreats, whether in private residences or commercial venues. Backlighting enhances inherent beauty of Himalayan Salt Bricks, casting soft ambient glow that creates calm and cozy atmosphere. Designers often pair such walls with wooden beams or neutral fabrics to amplify rustic yet sophisticated vibe, making spaces feel grounded and serene.Versatility of Himalayan Salt Bricks extends beyond full walls. Salt Tiles cut from same material serve as backsplashes, accent panels or floor inlays, adding subtle texture without overwhelming overall design. In spas and wellness centers, these tiles integrate seamlessly into holistic aesthetics, complementing natural elements like plants and stone. Their ability to diffuse light gently makes them ideal for areas meant for relaxation and unwinding.Himalayan Salt Bricks also shine as standalone decor pieces. Artisans carve them into candle holders, small sculptures and display accents, each piece boasting unique patterns and color variations. These items add warmth to coffee tables, mantels and shelving units, tying together design themes in living rooms, bedrooms and offices. Soft glow from candlelit salt holders creates intimate ambiance for gatherings or quiet evenings at home.Design flexibility of Himalayan Salt Bricks allows adaptation to diverse styles. For modern minimalist spaces, smooth-finish Salt Bricks offer streamlined look that complements clean lines and simple furnishings. Rustic interiors benefit from rough-hewn versions, which emphasize natural, unrefined beauty. Even commercial spaces like boutiques and cafes use these bricks to craft memorable environments that resonate with customers seeking authentic experiences.Preserving beauty of Himalayan Salt Bricks requires simple care practices. Keeping them away from excessive moisture prevents degradation, ensuring longevity in various settings. Regular dusting maintains their natural luster, allowing mineral-rich colors to remain vibrant over time. Such low-maintenance quality makes them practical choice for busy homes and high-traffic commercial areas alike.Global interest in warm modernism and natural design elements has elevated Himalayan Salt Bricks to must-have decor items. Their ability to infuse spaces with warmth, texture and unique visual appeal transcends fleeting trends. Whether used to build striking Salt Walls, craft delicate accents or line serene spa interiors, these bricks bring touch of mountain-inspired tranquility to any environment. As design preferences continue to prioritize comfort and authenticity, Himalayan Salt Bricks remain enduring choice for those seeking to transform spaces into havens of style and calm.Salt Tiles and bricks also offer customization possibilities. Artisans can shape them into various sizes and configurations, catering to specific design visions. From small accent pieces to full-wall installations, each application highlights distinct qualities of Himalayan Salt Bricks. Their natural color variations ensure no two installations are identical, adding exclusivity to every project. This uniqueness makes them beloved by designers and homeowners aiming to create personalized spaces that reflect individual taste.
Global interest in warm modernism and natural design elements has elevated Himalayan Salt Bricks to must-have decor items in recent years. Their ability to infuse spaces with warmth, texture and unique visual appeal transcends fleeting trends, making them enduring addition to any interior. Whether used to build striking Salt Walls, craft delicate accents or line serene spa interiors, these bricks bring touch of mountain-inspired tranquility to any environment. Interior designers increasingly recommend Himalayan Salt Bricks to clients seeking to balance modern functionality with natural charm, as they bridge gap between style and comfort. As design preferences continue to prioritize comfort and authenticity over overly polished aesthetics, Himalayan Salt Bricks remain enduring choice for those seeking to transform spaces into havens of style and calm.Salt Tiles and bricks also offer customization possibilities that cater to unique design visions. Artisans can shape them into various sizes and configurations—from thin panels for accent walls to thick blocks for statement pieces—adapting to specific space requirements. Some artisans add subtle engravings or cutouts to Himalayan Salt Bricks, creating patterns that interact beautifully with light. From small accent pieces to full-wall installations, each application highlights distinct qualities of Himalayan Salt Bricks. Their natural color variations ensure no two installations are identical, adding exclusivity to every project. This uniqueness makes them beloved by designers and homeowners aiming to create personalized spaces that reflect individual taste, rather than cookie-cutter interiors. Custom Salt Brick installations often become conversation starters, adding personal touch to homes and commercial venues alike.Salt Walls built with Himalayan Salt Bricks have become focal points in warm modernism designs. These structures transform ordinary rooms into inviting retreats, whether in private residences or commercial venues. Backlighting enhances inherent beauty of Himalayan Salt Bricks, casting soft ambient glow that creates calm and cozy atmosphere. Designers often pair such walls with wooden beams or neutral fabrics to amplify rustic yet sophisticated vibe, making spaces feel grounded and serene.Versatility of Himalayan Salt Bricks extends beyond full walls. Salt Tiles cut from same material serve as backsplashes, accent panels or floor inlays, adding subtle texture without overwhelming overall design. In spas and wellness centers, these tiles integrate seamlessly into holistic aesthetics, complementing natural elements like plants and stone. Their ability to diffuse light gently makes them ideal for areas meant for relaxation and unwinding.Himalayan Salt Bricks also shine as standalone decor pieces. Artisans carve them into candle holders, small sculptures and display accents, each piece boasting unique patterns and color variations. These items add warmth to coffee tables, mantels and shelving units, tying together design themes in living rooms, bedrooms and offices. Soft glow from candlelit salt holders creates intimate ambiance for gatherings or quiet evenings at home.Design flexibility of Himalayan Salt Bricks allows adaptation to diverse styles. For modern minimalist spaces, smooth-finish Salt Bricks offer streamlined look that complements clean lines and simple furnishings. Rustic interiors benefit from rough-hewn versions, which emphasize natural, unrefined beauty. Even commercial spaces like boutiques and cafes use these bricks to craft memorable environments that resonate with customers seeking authentic experiences.Preserving beauty of Himalayan Salt Bricks requires simple care practices. Keeping them away from excessive moisture prevents degradation, ensuring longevity in various settings. Regular dusting maintains their natural luster, allowing mineral-rich colors to remain vibrant over time. Such low-maintenance quality makes them practical choice for busy homes and high-traffic commercial areas alike.Global interest in warm modernism and natural design elements has elevated Himalayan Salt Bricks to must-have decor items. Their ability to infuse spaces with warmth, texture and unique visual appeal transcends fleeting trends. Whether used to build striking Salt Walls, craft delicate accents or line serene spa interiors, these bricks bring touch of mountain-inspired tranquility to any environment. As design preferences continue to prioritize comfort and authenticity, Himalayan Salt Bricks remain enduring choice for those seeking to transform spaces into havens of style and calm.Salt Tiles and bricks also offer customization possibilities. Artisans can shape them into various sizes and configurations, catering to specific design visions. From small accent pieces to full-wall installations, each application highlights distinct qualities of Himalayan Salt Bricks. Their natural color variations ensure no two installations are identical, adding exclusivity to every project. This uniqueness makes them beloved by designers and homeowners aiming to create personalized spaces that reflect individual taste. -

Talc powder for automotive plastics coatings paper ceramics and rubber industrial applications enhancing material performance stability
Talc powder is naturally occurring mineral formed from the weathering of magnesium silicate rocks, boasting distinctive physical and chemical traits that make it indispensable in diverse industrial fields. It typically appears as fine white or gray powder with greasy texture, soft consistency and excellent lubricity—traits that stem from its platy crystal structure. Such unique characteristics enable talc powder to blend seamlessly with various materials, not just mixing well but also delivering enhanced performance and processing convenience to end products. Its inherent chemical inertness ensures stable compatibility with most substrates, avoiding unwanted reactions even in long-term use, while reliable heat resistance and electrical insulation properties further expand its application scope in high-demand manufacturing processes across different sectors.Plastics industry relies heavily on talc powder as functional filler and reinforcement agent, especially in automotive plastic components. Talc powder integrates seamlessly into thermoplastics like polypropylene and polyethylene, effectively improving dimensional stability by minimizing warpage and reducing shrinkage during injection molding and extrusion processes. It significantly enhances heat resistance of plastic components, making them suitable for automotive parts that endure frequent mechanical stress and temperature fluctuations, such as dashboards, door panels and underhood components. Talc powder’s platy structure boosts stiffness and impact resistance of plastics without adding excessive weight, perfectly supporting lightweight strategies in vehicle manufacturing. This weight reduction helps lower fuel consumption and improve overall operational efficiency, aligning with modern automotive production trends focused on sustainability. Additionally, talc powder acts as a processing aid, reducing friction between plastic melts and mold surfaces, which shortens molding cycles and increases production efficiency for plastic manufacturers.Coatings and paints sector benefits greatly from talc powder’s unique properties, serving as a versatile mineral filler in both industrial and architectural coatings. As mineral filler, talc powder improves paint flowability and leveling, effectively preventing sagging and dripping during application on vertical or curved surfaces. It enhances hiding power and adhesion of coatings, forming a smooth, even and durable film that adheres tightly to various substrates like metal, wood and concrete. Talc powder’s platy particles also help maintain uniform pigment dispersion, ensuring consistent color and finish across all coated products, avoiding streaks or uneven shading. Beyond aesthetics, it boosts resistance to water, acids and abrasion, extending service life of coatings used in industrial structures, machinery and outdoor equipment. Primers and intermediate coatings frequently incorporate talc powder to optimize sedimentation resistance—preventing filler particles from settling at the bottom of paint cans—and improving re-coatability, allowing subsequent layers to bond firmly, all while meeting strict quality standards of manufacturing industries.Paper industry has long utilized talc powder for improving product quality and processing efficiency across various paper grades. Talc powder acts as both filler and coating agent, enhancing brightness, opacity and smoothness of paper—key attributes for printing and packaging papers. When used as filler, it fills gaps between cellulose fibers, creating a denser structure that strengthens paper’s ability to absorb printing inks, ensuring vivid color reproduction, sharp print quality and faster drying times. As coating agent, it forms a thin, smooth layer on paper surfaces, reducing ink penetration and improving print clarity. Talc powder also functions as essential resin control additive, absorbing residual resins and pitch in pulp to prevent machine jams, sticky rollers and surface defects like spots or streaks. In waste paper recycling processes, talc powder aids in deinking by breaking down ink particles and detackifying sticky contaminants, significantly improving pulp purity and resulting recycled paper quality. These diverse applications make talc powder a key component in producing various paper products, from high-gloss printing papers and packaging materials to tissue papers and corrugated cardboard.Ceramics manufacturing leverages talc powder to adjust product properties and optimize processing parameters, reducing production costs while enhancing end-product performance. Adding talc powder to ceramic blanks lowers firing temperature by several degrees and widens the acceptable temperature range during firing, which not only reduces energy consumption but also minimizes the risk of product deformation or cracking. Small amounts of talc powder enhance transparency, mechanical strength and thermal stability of ceramics, making them suitable for industrial components and decorative items alike. Higher concentrations of talc powder facilitate formation of special crystals like enstatite, improving thermal shock resistance and dielectric properties—critical for ceramics used in electrical and high-temperature environments. Talc powder also serves as effective flux in glazes, reducing melting temperature, improving glaze elasticity and preventing crazing. It adds natural opacity to matte glazes, creating desired textures and finishes, while meeting both aesthetic and functional requirements of ceramic products for industrial machinery parts and construction materials like floor tiles and wall cladding.Rubber industry uses talc powder extensively as functional filler and insulation material, enhancing both product performance and processing feasibility. It penetrates rubber matrices to enhance mechanical strength, tear resistance and internal lubrication, improving overall durability and reducing wear and tear during long-term use. This lubricating effect also simplifies processing, reducing energy consumption during mixing, calendering and molding stages. Talc powder significantly boosts electrical insulation of rubber products, making it ideal for cable insulation, rubber gaskets and other rubber components used in electrical equipment and power transmission systems. It also acts as reliable anti-sticking agent, forming a thin protective layer on rubber surfaces that prevents products from adhering to molds, machinery or each other during production, storage and transportation. Strict quality control measures ensure talc powder meets precise purity and particle size requirements for rubber applications, as inconsistent particle distribution can affect rubber’s flexibility and performance, maintaining uniformity and reliability in end product performance.Waterproof materials production incorporates talc powder to enhance product reliability, durability and weather resistance, catering to construction and industrial waterproofing needs. It is widely added to asphalt membranes, acrylic coatings and polyurethane sealants, where it improves flexibility and elongation at break—allowing waterproof materials to adapt to structural movements without cracking. Talc powder strengthens bonding between material components, creating a seamless barrier that prevents water leakage and extends service life of waterproof systems in demanding settings like rooftops, basements, industrial tanks and bridges. Its chemical stability ensures waterproof materials maintain consistent performance under harsh environmental conditions, including extreme temperature changes, prolonged moisture exposure, UV radiation and chemical erosion. Additionally, talc powder improves rheological properties of waterproof formulations, preventing settling of heavy components and ensuring uniform application, which further enhances the effectiveness of waterproof layers.Global demand for talc powder continues to grow, driven by expanding manufacturing sectors and technological advancements in processing. Talc powder’s versatility and cost-effectiveness make it preferred choice for manufacturers seeking to optimize product performance and production efficiency. Strict quality standards and testing procedures ensure talc powder meets industry-specific requirements, eliminating contaminants and ensuring safety in applications. -

Kaolin powder boost adhesion enhance thermal stability strengthen composite rigidity optimize refractory performance stabilize sealant flexibility improve polymer durability upgrade asphalt quality
Kaolin Powder is naturally occurring non-metallic mineral dominated by kaolinite, formed through gradual decomposition and transformation of feldspar-rich aluminosilicate rocks under combined action of water, wind and biological factors over millions of years. It features soft, silky texture that feels smooth to touch, fine plate-like particles with ultra-thin lamellar structure (which can overlap and interlock) and synergistic physical-chemical properties that underpin its wide industrial value. Core traits include inherent whiteness that avoids discoloration of light-toned or transparent end products, excellent plasticity that enables easy shaping in semi-solid systems (such as sealant pastes) without cracking, stable chemical inertness that resists reactions with common industrial reagents like resins, solvents and plasticizers, and strong lamellar bonding that enhances formulation stability and anti-settling ability. These natural properties, combined with customizable processing technologies, allow it to integrate seamlessly into diverse industrial chains without disrupting core functions of base materials, acting as silent performance booster that upgrades product quality.Processing techniques of kaolin powder are meticulously tailored to unlock targeted functionalities for different industrial needs. Washing, as foundational purification step, involves crushing raw ore into small fragments first, then mixing with water to form uniform slurry. This slurry is then passed through high-speed centrifugal separation equipment to remove heavier impurities, coarse grains and organic contaminants—this method improves purity and particle size uniformity more efficiently than traditional gravity separation, making it ideal for color-sensitive applications like light-toned plastic products. Calcining is a key step for enhancing high-temperature performance: particles are heated in sealed kilns under strictly controlled temperature and atmosphere conditions to eliminate internal moisture and organic matter. This process induces subtle changes in crystal structure, transforming kaolin into metakaolin that boasts significantly boosted hardness, thermal stability and opacity—critical for high-temperature scenarios such as refractory materials. Surface modification is essential for compatibility with organic matrices: particles are coated with silane coupling agents in high-speed mixers, forming a thin functional layer on the surface that improves bonding with polymers and resins. This modification effectively prevents particle agglomeration and maximizes reinforcing effects in composite materials. Each processing step is dynamically adjusted based on specific end-use requirements, ensuring kaolin powder delivers optimal performance across various industrial sectors.Adhesive and sealant industry relies heavily on kaolin powder to solve key formulation pain points in industrial scenarios. It precisely adjusts viscosity of adhesive formulations to the ideal range—preventing sagging or dripping during vertical application on mechanical parts (such as engine components) while maintaining appropriate smoothness for bonding irregular pipe joints (common in chemical plants). Fine particle size and strong suspension ability of kaolin powder keep formulations uniform and stable during long-term storage (whether in sealed barrels or flexible tubes), avoiding sedimentation or stratification that causes uneven bonding strength. Kaolin powder enhances bonding strength through dual mechanisms: its ultra-fine particles penetrate deeply into tiny pores and crevices of substrates—whether metal (steel, aluminum), plastic (polypropylene, PVC) or wood (plywood, solid wood)—forming tight mechanical interlocks; meanwhile, its surface functional groups (after modification) form weak chemical bonds with substrate surfaces, jointly resisting peeling, shearing and corrosion from industrial chemicals (such as solvents and acids). In sealants used for chemical equipment (reactors, storage tanks), it significantly boosts temperature resistance and chemical stability, allowing sealants to withstand harsh working environments (high temperature, corrosive gas) without cracking or losing elasticity, effectively protecting equipment from leakage and ensuring production safety.Refractory materials sector values kaolin powder’s exceptional thermal stability and anti-spalling ability more than any other industry. When mixed with alumina and magnesia in scientific proportions (adjusted based on specific equipment needs), it forms high-performance blends for manufacturing refractory castables and furnace linings—focused on key equipment such as glass melting furnaces (which operate at extremely high temperatures) and cement rotary kilns (subject to frequent temperature changes). These blends, with kaolin powder as core functional component, can retain stable structural integrity even under extreme heat, forming dense protective barriers that shield furnace walls from severe thermal shock (caused by sudden temperature rises or drops) and corrosion from harmful gases (released during melting or calcining processes). Kaolin powder’s unique lamellar structure fills tiny gaps between coarse refractory particles, greatly improving density of refractory products and reducing heat loss from furnaces—helping enterprises save energy. More importantly, its excellent anti-spalling trait prevents material peeling or cracking caused by repeated temperature cycles, significantly extending service life of refractory linings and reducing maintenance downtime and replacement costs for factories.Plastic industry widely uses kaolin powder as cost-effective reinforcement to upgrade comprehensive performance of basic plastics. When added to polypropylene and polyethylene (the most commonly used general-purpose plastics), it significantly enhances rigidity of plastic products—making them suitable for manufacturing household appliance casings (refrigerators, washing machines) and construction plastic profiles (door and window frames). It also improves heat resistance of plastics, enabling them to be used in manufacturing electrical component housings (which generate heat during operation) without deformation. Additionally, kaolin powder boosts dimensional stability of plastics, preventing warping or shrinking after molding—critical for precision plastic parts. Surface-modified kaolin powder can disperse evenly in polymer matrices, forming strong interfacial bonds that increase impact resistance while maintaining surface smoothness—essential for appearance-sensitive products (such as plastic decorative parts). Importantly, it is fully compatible with existing extrusion and injection molding processes, allowing manufacturers to use existing equipment without additional modifications or production costs.Composite materials industry leverages kaolin powder to perfectly balance performance, cost and weight—three core demands in composite manufacturing. In fiber-reinforced composites used for wind turbine blades (which require high strength and light weight) and automotive lightweight parts (aimed at reducing fuel consumption), kaolin powder acts as functional filler that not only enhances rigidity, fatigue resistance and dimensional stability of composites but also effectively reduces overall weight. It can replace part of expensive carbon fibers or glass fibers in composite formulations, significantly lowering production costs without compromising structural strength. Kaolin powder’s plate-like particles can align parallel to composite matrices during processing, forming a “lamellar reinforcement network” that improves stress distribution—effectively transferring external forces to fiber components, preventing localized damage (such as fiber breakage or matrix cracking) and extending service life of composite components under long-term cyclic loads (common in wind turbine operation and automotive driving).Asphalt modification sector (a new application to differ from previous texts) enthusiastically embraces kaolin powder for its unique ability to upgrade road performance comprehensively. When added to asphalt mixtures (the main material for road construction), it significantly enhances high-temperature stability of asphalt, reducing the risk of rutting (formed by heavy traffic) on roads in hot climates (such as tropical or subtropical regions). Its lamellar structure can form a dense protective network in asphalt, improving anti-aging performance (resisting oxidation from sunlight and air) and water resistance (preventing water from penetrating into road layers)—greatly extending road service life. Kaolin powder also adjusts asphalt viscosity to the optimal range, optimizing construction workability (making it easier to pave and compact) without affecting final hardness of the road surface. This application is widely used in highway and urban road construction, especially in key projects requiring high durability (such as expressways and airport runways), perfectly meeting demands for reliable and long-lasting transportation infrastructure. -

Colored sand glow bright in kids classrooms shop windows art therapy festival fun micro worlds where colors mix with textures spark joy for daily little creations colored sand
Colored sand has super fun magic that turns boring little moments into awesome creative adventures. It’s not just for craft tables or home shelves—you’ll find it popping up in all kinds of unexpected spots, blending with daily activities to bring big smiles and cool ideas. Run fingers through it, and it sifts through gently, like tiny rainbow bits dancing between digits. Those soft grains and bright, happy hues make it super versatile—fits right into so many things without losing that cozy, fun charm everyone loves.Schools and preschools totally love using colored sand for fun learning. They fill big bins with it—called sensory bins—and let little kids dig, sift, and play to get better at using their tiny hands, all while gawking at all the pretty colors. Teachers turn lessons into games: kids trace letters or draw shapes in sand while singing songs, making math and reading feel like playtime, not work. Sometimes everyone teams up to make huge sand murals—each kid dumps their favorite color, and together they make something awesome, learning to share and talk with each other along the way. It’s how learning should be—fun, messy, and full of giggles, with sand making every step feel like an adventure.Shop windows use colored sand to grab attention—like little colorful magnets for passersby. Cute boutiques change their displays with seasons: soft pastels for spring dresses, warm oranges and browns for autumn sweaters—arranged into tiny scenes, like sand flowers or mini pumpkins, that match what they’re selling. Cosmetic stores get clever too—they use shimmery sand to look like highlighter, or matte sand to mimic lipstick texture, so you can instantly get what the products feel like. Even cafes and bookstores join in, decorating windows with sand art—quotes from favorite books or tiny coffee cups drawn in sand—making you stop, smile, and maybe pop in for a drink or a book. It turns boring storefronts into little art shows everyone can enjoy.Art therapy sessions use colored sand to help people relax and let out their feelings—no fancy words needed. Therapists say things like, “Grab that sand, pour it, mix it, make whatever feels right,” and people do just that. Pouring sand from one jar to another, swirling colors together, or making simple dots and lines—those slow, easy motions make stress melt away. Clients say handling sand feels like a hug for the mind; focusing on how soft it is and how pretty the colors are makes all the worries fade. Bright yellows and pinks for happy days, soft blues and purples for calm moments, deep greens for when you’re thinking hard—sand lets you show how you feel without saying a thing. It’s a simple, gentle way to feel better, one grain at a time.Festivals get way more fun with colored sand sprucing things up. Music festivals line stages and walkways with it—some even use glow-in-the-dark sand that lights up at night, making the whole place look like a fairyland. Cultural festivals mix sand into their traditions, with different colors standing for happy things like good luck or friendship. Halloween uses dark, spooky sand shaped into little ghosts or pumpkins, and Christmas has white and red sand made into tiny snowmen or candy canes. People even add sand to their festival outfits—sew little packets of it into hems or pin them to hats—so they jingle a little and look extra festive as they dance or walk around. Sand turns regular festivals into memories you’ll talk about forever.People who love making tiny worlds—micro landscapes—swear by colored sand. They grab glass jars or boxes, layer sand in different colors: blue for oceans, green for grass, brown for dirt, and white for little snow-capped mountains. Then they add tiny plants, little rocks, or even mini toy people and houses to make the scene feel real. These tiny masterpieces sit on desks or shelves, bringing a little bit of nature into apartments or offices. Fans love sharing tips online too—like how to mix sand with glue to keep layers from shifting, or how to add tiny lights to make the whole thing glow. It’s a super chill hobby that lets you be a tiny god of your own little colorful world.Colored sand even pops up in photos and movies—making regular shots look way cooler. Photographers lay jewelry, small gadgets, or even makeup on beds of colored sand to take product photos; a little necklace on pink sand or a phone on blue sand instantly makes the item look more fun and eye-catching. Filmmakers use sand to make sets look real—desert scenes with golden sand, beach scenes with mixed tan and blue sand—or to add symbolic touches, like sand flowing to show time passing. Some music videos have sand art performances too: artists draw pictures in sand that change as the song plays, telling stories with colors and shapes. It’s crazy how sand turns regular visuals into something everyone stops to watch.What makes colored sand stick around is that it’s simple but totally amazing. You don’t need to be a pro to use it—just grab some, play around, and see what happens. Kids love it, adults love it, and everyone in between finds joy in its colors and texture. In a world where everything feels so complicated with phones and computers, sand is a breath of fresh air. It’s humble, it’s cheap, but it can make any day brighter and any space more fun. It keeps popping up in new places, bringing color and smiles wherever it goes—and that’s why everyone loves it so much. -

Iron oxide pigments for architectural coatings industrial finishes construction materials artistic creations outdoor decor
Iron oxide pigments stand as essential components in numerous industries, offering rich, stable colors that enhance appearance and durability of various products. These pigments derive from natural or synthetic sources—natural variants extracted from mineral deposits, synthetic ones produced through controlled chemical reactions—boasting unique properties that make them indispensable in fields ranging from construction to art. Unlike many other colorants, iron oxide pigments resist fading caused by sunlight, moisture, and extreme temperature changes, ensuring long-lasting vibrancy in diverse environments, from arid deserts to humid coastal areas. Their compatibility with different substrates—including concrete, metal, wood, and plastics—also makes them versatile choice for professionals and enthusiasts alike, seamlessly integrating into various production and creative processes without compromising performance.Architectural coatings represent one of primary applications for iron oxide pigments. Paints and primers containing these pigments adorn exteriors and interiors of buildings, providing not only aesthetic appeal but also robust protection against harsh elements such as acid rain and industrial pollutants. Exterior wall paints infused with iron oxide pigments maintain their color even after years of exposure to rain, snow, and UV rays, reducing need for frequent repainting and lowering long-term maintenance costs. Interior spaces benefit from warm, earthy tones of iron oxide pigments—shades like terracotta, ochre, sienna, and burnt umber add warmth to living rooms, bedrooms, and commercial lobbies, creating cozy and inviting atmospheres. Decorative coatings for ceilings, columns, and moldings also use these pigments to create textured or matte finishes; when mixed with inert fillers, they form finishes that mimic natural stone, elevating overall design while maintaining affordability.Industrial finishes rely heavily on iron oxide pigments to enhance both function and appearance of machinery, equipment, and metal structures. Manufacturers incorporate these pigments into coatings for automotive parts (such as wheel rims and undercarriage components), farm machinery exposed to outdoor elements, and industrial pipes transporting fluids—forming protective barrier against rust and corrosion that extends service life of these products. Color coding of industrial components also uses iron oxide pigments—distinct hues (like rust red, deep brown, and olive green) help workers identify different parts, pipelines, and safety equipment quickly, improving safety and efficiency in factories and construction sites. Even metal furniture and appliances feature finishes containing iron oxide pigments, as they resist scratches, stains, and daily wear, maintaining sleek appearance over time while withstanding frequent cleaning.Construction materials represent another major area where iron oxide pigments shine. Concrete products such as paving stones, bricks, roof tiles, and decorative aggregates are often colored with these pigments, transforming plain gray material into visually appealing elements that blend with surrounding landscapes. Colored concrete pavers line walkways, driveways, and plaza floors, adding character to residential and commercial properties while resisting abrasion from foot and vehicle traffic. Roof tiles tinted with iron oxide pigments not only complement building exteriors but also reflect sunlight to reduce indoor temperatures, contributing to energy efficiency in buildings. Even precast concrete elements like fences, retaining walls, and decorative panels use these pigments to match architectural styles—from modern minimalist designs with bold, solid colors to traditional styles mimicking natural stone textures—without sacrificing structural integrity.Artistic creations and crafts benefit greatly from unique properties of iron oxide pigments. Artists have used natural iron oxide pigments for centuries—valued for their opacity and lightfastness—as they blend easily with binders (such as linseed oil for oils, gum arabic for watercolors) to create oil paints, watercolors, pastels, and even frescoes. These pigments offer rich, earthy tones that add depth and realism to landscapes (capturing soil and rock hues), portraits (enhancing skin tones), and abstract works (providing bold, grounded colors). Crafters incorporate iron oxide pigments into pottery and ceramics, applying them as glazes or underglazes; when fired, pigments fuse with clay surfaces to create intricate patterns and textures that resist chipping. Even DIY projects like homemade candles, soap, resin art, and handmade paper use these pigments to add color, as they mix well with different mediums, retain their hue without bleeding, and remain stable under varying conditions.Outdoor decor and landscaping projects also leverage durability and color stability of iron oxide pigments. Garden ornaments such as statues, planters, birdbaths, and decorative fountains are coated with pigments to resist fading, weathering, and mold growth, ensuring they remain attractive in gardens for years regardless of sun exposure or rainfall. Colored mulch and decorative stones treated with iron oxide pigments add pops of color to flower beds, borders, and pathways, enhancing overall beauty of outdoor spaces while resisting leaching of color into soil. Public parks and recreational areas use these pigments in decorative concrete elements like benches, picnic tables, and playground surfaces—formulating them into non-slip coatings that withstand heavy use, extreme temperatures, and frequent exposure to water, ensuring safety and longevity.Another advantage of iron oxide pigments is their exceptional consistency in color. Unlike natural dyes that vary in shade due to differences in source materials and extraction processes, these pigments undergo strict quality control during production, offering uniform color batches that match precise specifications. This consistency ensures that products maintain consistent appearance across production runs—critical for industries like construction (where matching wall paints or concrete elements across large projects is essential) and automotive (where replacement parts must blend seamlessly with original finishes). Professionals trust iron oxide pigments to deliver predictable results, reducing rework, saving time, and minimizing material waste that comes with color mismatches. -

Natural and artificial black rubber granules core materials for road construction and artificial grass applications
Rubber granules derive primarily from recycled waste tyres and other rubber products, undergoing processes like mechanical crushing and chemical modification to form particles of varying sizes. These versatile materials have gained widespread attention across multiple industries due to their unique physical properties and cost-effective advantages.In road construction sector, rubber granules play a pivotal and irreplaceable role in modifying asphalt and enhancing comprehensive pavement performance. When evenly blended with bitumen, rubber granules not only improve the elasticity and deformation resistance of asphalt mixtures significantly but also enhance the mixtures’ ability to withstand repeated vehicle loads, thereby reducing the occurrence of rutting, cracking, and potholes under extreme temperature changes—whether it is the high-temperature baking in summer or the low-temperature freezing in winter. Such modified asphalt further exhibits superior fatigue resistance and water damage resistance, which can effectively extend the overall service life of road surfaces by 30% to 50% compared with traditional asphalt pavements. Recent large-scale trials in rural road sealing projects in multiple regions have demonstrated that incorporating rubber granules as aggregate substitutes not only reduces the consumption of natural aggregates but also effectively lowers maintenance needs and eliminates dust emissions, bringing practical and tangible benefits to local residents’ travel and daily life. The preparation of rubber asphalt requires precise control of mixing temperature, mixing time, and other key conditions to ensure the uniform dispersion of rubber granules in the bitumen matrix, thereby maximizing their performance-enhancing effects and avoiding local agglomeration that may affect pavement quality.Sports and recreation facilities represent another major and fast-growing application area for rubber granules. As a core infill material for artificial grass, rubber granules fill the gaps between artificial grass fibers, providing soft, shock-absorbent, and anti-slip playing surfaces. This not only improves the safety of athletes during sports—effectively reducing the risk of falls and injuries—but also enhances the overall playing experience by simulating the feel of natural grass. Colored rubber granules, which are processed by adding environmentally friendly pigments during production and available in various vivid hues like green, red, blue, and yellow, are widely used in the construction of running tracks, football fields, tennis courts, and children’s sports grounds. These colored rubber granules not only meet the aesthetic and functional partitioning requirements of sports venues but also possess excellent properties such as wear resistance, UV protection, flame retardancy, and weather resistance, ensuring that the color and performance of the venue surface remain stable for a long time. EPDM rubber granules, a specific type of high-performance synthetic rubber granules, are particularly favored in professional sports facilities due to their outstanding oxidation resistance, ozone resistance, and low-temperature flexibility. Even under harsh environmental conditions such as strong ultraviolet radiation, heavy rainfall, and large temperature differences, EPDM rubber granules can maintain their structural integrity and performance stability, ensuring the long-term durability of sports facilities.Production technologies of rubber granules continue to innovate and evolve, with physical crushing and low-temperature freezing crushing being the mainstream methods in the industry. Physical crushing technology, which typically includes processes such as tire shredding, steel wire separation, and granulation, is widely used due to its mature process and low production cost. However, it may cause partial aging of rubber due to the friction heat generated during crushing. In contrast, low-temperature freezing crushing technology uses liquid nitrogen to quickly cool waste rubber to a brittle state, then crushes it into granules. This method minimizes rubber aging during processing, producing granules with regular shapes, uniform particle sizes, and rough surfaces that can bond more firmly with other materials. After the initial crushing, subsequent grading and screening processes, which use multi-layer sieves of different meshes, classify rubber granules into various size ranges to precisely adapt to diverse application needs—for example, fine rubber granules with particle sizes below 1mm are suitable for asphalt modification, medium-sized granules of 1-3mm are used for artificial grass infill, and coarse granules above 3mm are applied for road base filling and shock absorption layers. In addition, chemical modification technologies such as surface activation and grafting modification further enhance the compatibility and bonding strength between rubber granules and bitumen, polymer materials, and other substrates, optimizing the overall performance of composite materials and expanding the application boundaries of rubber granules.The global rubber granules market is experiencing steady and sustained growth, driven by the increasing global infrastructure construction investment, the continuous expansion of sports and recreation facility construction, and the growing emphasis on waste tyre recycling. North America and Europe remain the dominant markets for rubber granules, thanks to their mature waste recycling systems, strict environmental regulations, and high demand for high-quality sports facilities. In these regions, the application of rubber granules in road construction and professional sports venues is highly standardized. Meanwhile, the Asia-Pacific region shows strong and rapid growth momentum, fueled by the accelerating urbanization process, large-scale road network construction, and the rising popularity of sports activities in emerging economies such as China, India, and Southeast Asian countries. Major market players in the global rubber granules industry are focusing on technological innovation to improve product quality and production efficiency, as well as capacity expansion to meet the growing market demand. Industry collaboration has also become a key trend—raw material suppliers, production enterprises, and downstream application companies are strengthening cooperation to optimize the supply chain, address the variability of waste tyre raw materials, and jointly promote the standardization and upgrading of the rubber granules industry.Despite their widespread applications and significant market potential, rubber granules still face certain challenges and bottlenecks in the process of industrial development. One of the key challenges is odor control during processing and application. During the production of rubber granules, especially high-temperature processing processes, and when used in high-temperature environments such as summer road surfaces or enclosed sports venues, rubber granules may release volatile organic compounds, resulting in unpleasant odors that affect user experience. Another major challenge is the optimization of dosage in different mixtures. The optimal dosage of rubber granules varies significantly depending on the application scenario—for example, the dosage in asphalt modification is different from that in artificial grass infill, and excessive or insufficient dosage may seriously affect the performance of end products, such as reducing pavement strength or decreasing shock absorption effect. This requires ongoing in-depth research and a large number of experimental verifications to determine the precise optimal proportions for different application scenarios. Additionally, the establishment of unified and authoritative industry standards and testing methods remains an urgent task globally. -

Exploring the diverse applications and environmental benefits of recycled black rubber granules
Black rubber granules are tiny, spherical particles made from recycled rubber materials, usually sourced from discarded automobile tires. These granules are a versatile and eco-friendly product that offers numerous benefits and applications.
One of the primary uses of black rubber granules is in the construction of artificial turf fields. These fields, often used in sports such as soccer, football, and hockey, require a stable and shock-absorbent base layer. Black rubber granules provide the perfect solution, as they enhance the cushioning properties of the turf and reduce the risk of injuries to athletes. The black color of the granules also helps to absorb heat, which can improve the melting point of the turf and extend its lifespan.
In addition to sports fields, black rubber granules are also used in playground surfacing, landscape mulching, and road construction. In playgrounds, they offer a safe and durable surface that can withstand heavy foot traffic and provide excellent shock absorption. As landscape mulch, they help to retain soil moisture, suppress weed growth, and add a decorative touch to garden beds. In road construction, black rubber granules can be mixed with asphalt to create a quieter and more durable road surface.
-

Sepiolite Fiber Delivers Excellent Adsorption Capacity Filtration Performance and Structural Enhancement for Industrial Wastewater Treatment Building Materials and Air Purification Applications
Sepiolite fiber is a natural magnesium silicate mineral with distinctive layered chain structure. This structure forms numerous interconnected micro pores and channels, which give sepiolite fiber remarkable physical and chemical properties. Unlike many synthetic materials, sepiolite fiber exists naturally in earth, mainly found in clay deposits, and requires only purification and appropriate processing to unlock its multiple functions. Its appearance presents as slender needle like bundles that can disperse into individual fibers in polar solvents, forming interwoven networks that enhance performance of various products.Core advantage of sepiolite fiber lies in its outstanding adsorption capacity, derived from high specific surface area and abundant active hydroxyl groups on fiber surface. These hydroxyl groups can form hydrogen bonds with different substances, while multi level pore structure—including tiny internal channels and larger inter fiber pores—enables selective capture of impurities. In industrial wastewater treatment, this adsorption capacity becomes particularly valuable. Sepiolite fiber can target heavy metal ions, organic dyes, phenols and oil substances in wastewater, trapping them within its pore structure through physical adsorption and chemical complexation.Application in industrial wastewater treatment demonstrates practical value of sepiolite fiber. When added to reaction tanks or used as filter media in columns, it effectively reduces pollutant concentrations. Modified sepiolite fiber, treated with acids to expand pore size and remove impurities, shows even stronger adsorption performance. After adsorption saturation, sepiolite fiber can be regenerated through simple methods such as elution with salt solutions or heating, allowing repeated use and reducing waste. This regenerability makes it cost effective option for long term wastewater treatment operations, especially for small and medium sized factories.Building materials sector is another key area where sepiolite fiber excels, primarily through structural enhancement and performance optimization. When mixed into cement mortar or gypsum products, slender fibers of sepiolite form three dimensional supporting networks within matrix. These networks block formation and expansion of micro cracks, significantly improving mechanical strength—including compressive and flexural strength—of building materials. For cement mortar, adding appropriate amount of sepiolite fiber can increase flexural strength by over twenty five percent. Additionally, sepiolite fiber regulates moisture in building materials; it absorbs excess moisture in humid environments and releases it in dry conditions, reducing deformation caused by humidity fluctuations.In coatings and insulation materials, sepiolite fiber provides multiple benefits. In water based architectural coatings, its fiber structure creates thixotropic networks that prevent sagging during application while maintaining smoothness during brushing. This structure also prevents settling of pigments and fillers, extending storage stability of coatings. For insulation mortar, porous nature of sepiolite fiber reduces thermal conductivity, enhancing heat preservation effect, while its fiber skeleton prevents powdering of insulation layers, balancing insulation performance and mechanical strength. Fire retardant coatings also benefit from sepiolite fiber’s high temperature resistance, extending fire resistance time of coatings.Air purification represents another important application field for sepiolite fiber. Its adsorption capacity effectively captures harmful gases and particulate matter in air. When made into filter nets or combined with other materials in purification products, it removes volatile organic compounds and formaldehyde from indoor air. Sepiolite fiber also acts as catalyst carrier; loading metal oxides or photocatalysts onto its surface enables catalytic conversion of harmful substances into harmless ones. This combination of adsorption and catalysis makes sepiolite fiber based materials more thorough in air purification, avoiding secondary pollution issues associated with some adsorbents.Versatility of sepiolite fiber stems from synergy between its natural structure and adjustable properties. Its compatibility with other materials allows compounding with resins, clays and catalysts to create customized products for specific needs. Whether in environmental protection, construction or air treatment, sepiolite fiber plays role of functional enhancer, adsorbent or structural stabilizer. As research on modification technologies advances, potential applications of sepiolite fiber continue to expand, from high temperature sealing materials to new energy related fillers. This natural mineral fiber, with its inherent performance advantages and environmental friendliness, remains valuable resource across multiple industrial sectors.